Technical Differentiators¶
ScyllaDB is known for engineering optimizations that enable predictable performance at scale. If you are interested in database internals, we encourage you to browse our engineering blog, watch our tech talks from past and present conferences, and review our architecture details.
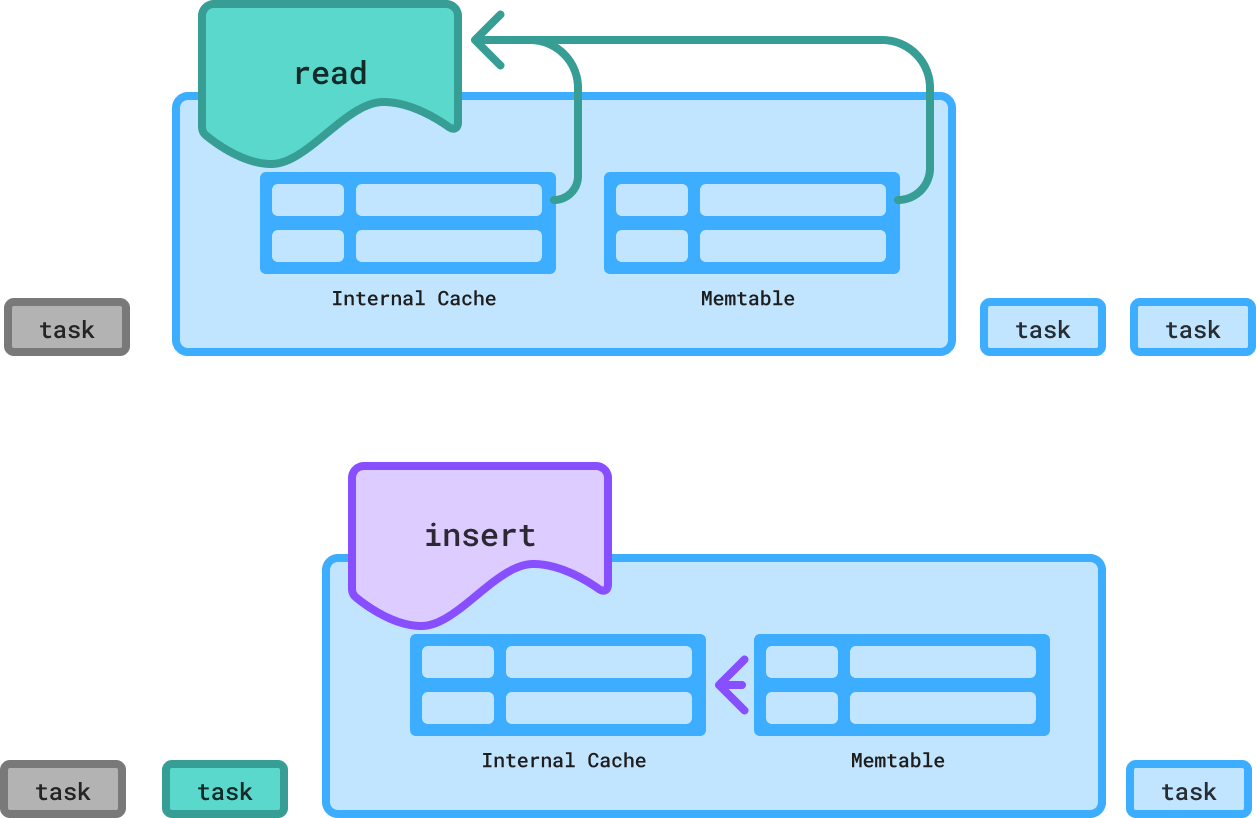
Internal Caching¶
ScyllaDB completely bypasses the Linux cache during reads and uses its own highly efficient row-based integrated internal cache instead. This unified cache can dynamically tune itself to any workload.
This provides ScyllaDB the control needed to deliver ultra-low latency without an external cache. It enables each ScyllaDB node to serve more data, which in turn lets users run smaller clusters of more powerful nodes with larger disks.
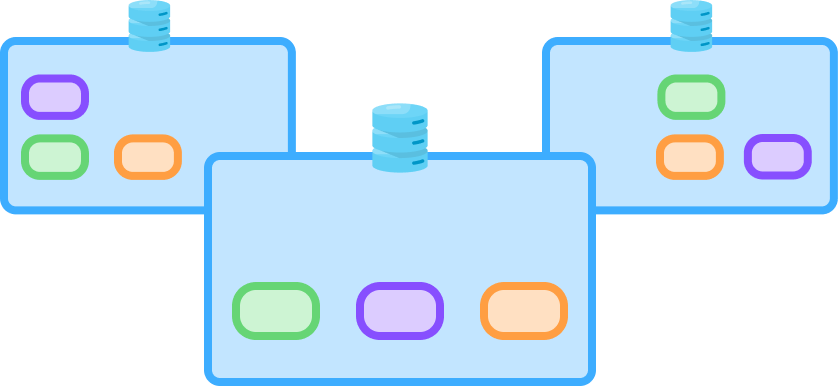
Tablets Elasticity¶
Each ScyllaDB table is split into smaller fragments (“tablets”) to evenly distribute data and load across the system. Tablets are then replicated to multiple ScyllaDB nodes for high availability and fault tolerance. This approach separates token ownership from servers – ultimately allowing ScyllaDB to scale faster and in parallel.
With tablets, data is dynamically redistributed as the workload and topology evolve. New nodes can be spun up in parallel and start adapting to the load in near real-time. This means teams can quickly scale out in response to traffic spikes – satisfying latency SLAs without needing to overprovision “just in case.”
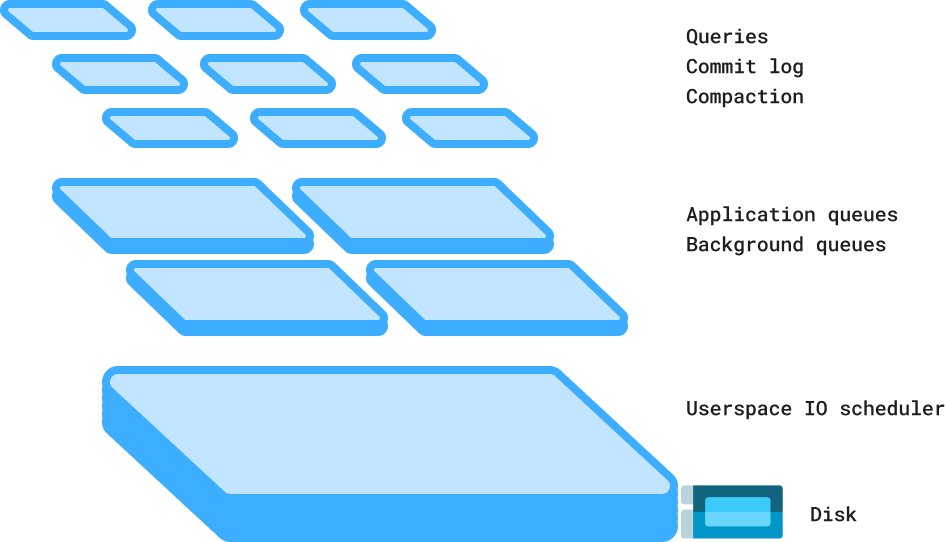
Schedulers¶
ScyllaDB uses its own built-in CPU and IO schedulers. It can automatically prioritize its own activities due to real-time, real-world conditions.
Even under the most intense workloads, ScyllaDB runs smoothly without requiring frequent administrator supervision and intervention.
Workload Prioritization¶
Workload Prioritization controls how different workloads compete for system resources. It’s used to prioritize urgent application requests that require immediate response times versus others that can tolerate slight delays (e.g., large scans).
Common use cases include balancing real-time vs batch processing, splitting writes from reads, and workload/infrastructure consolidation.